Source
Busy lifestyles, urbanization, and a globalized world have led to packaging of products becoming a necessity of day-to-day life, used to transport all types of materials. However, the flexible packaging market is growing at a far more rapid pace than rigid packaging, offering more potential across various industries.
The flexible packaging market size is estimated to reach a worth of $131.24 by 2022 growing at a CAGR of 4-4.45 percent, for a volume of 35.2 million metric tons (MMT). The market is driven by the food & beverages, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. In terms of volume, Asia is the largest regional market, followed by Western Europe and North America.
What Is Flexible Packaging?
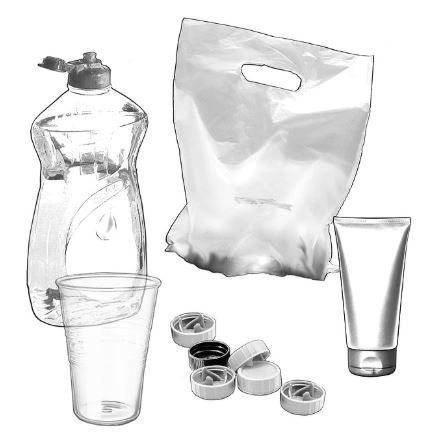
Flexible packaging can be defined as any package, such as bags, pouches, liners or overwraps, made of flexible material of which the shape can be easily changed. Typical materials used for flexible packaging include plastics, papers, films, aluminum foil, metals, and sheets. By combining additives to the material, the characteristics of flexible packaging can be further enhanced, making it resealable, printable, heating-friendly, food safe etc.
In general, flexible packaging offers immense overall flexibility, as the materials used can be modified and designed to accommodate any shape or size of the product. Flexible packaging is a low-cost alternative to rigid packaging and requires less energy in the manufacturing process and in transportation, generating smaller quantities of greenhouse gases.
Factors driving the flexible packaging market are its applications, regional growth and most importantly the sustainability it offers, which is further encouraging the growth of the field.
Applications
Due to its versatility, flexible packaging is used for consumer products, institutional products and in industrial applications for the purpose of transporting, protecting, marketing and distributing a variety of substances.
The single largest end-user segment is the food & beverages industry, since flexible packaging protects food and drink items from spoiling. The flexible packaging also allows individual portioning of items and directions can be printed directly on the packaging. Fresh fruits and vegetables, confectionary items, baked goods and even bulk items such as grains are packed in flexible packaging solutions such as bags and pouches. Processed foods are also packed in flexible packaging, extending their shelf-life and making transport easy.
Other major end-user industries for flexible packaging are pharmaceuticals and personal care items. Flexible packaging provides protection against light and oxygen, as well as resistance to moisture, reducing the risk of contamination to pharmaceuticals and personal care items. Pouches and sachets are becoming more common in both of the industries, replacing tubes, bottles and other hard plastic containers.
In an industrial landscape, flexible packaging is used for palletizing, wrapping and bundling of bulk containers, as a cost-effective and logistically viable alternative to rigid packaging.
Regional Markets
The market for flexible packaging is expected to witness consistent growth in developed and developing markets. Rapid economic development and increasing consumerism are driving the market in developing regions, for example, the MEA and APAC. Greater disposable income and awareness of the popularity of flexible packaging in developed countries further increase the demands in developing nations. Solid demands from the India and China markets are leading more flexible packaging converters to invest in the two nations.
The demand for flexible packaging continues to grow in developed markets such as North America and Europe, led by sustainability concerns. Regulations in place in developed markets for environment-friendly manufacturing also encourage the market for flexible packaging. Further possibilities of flexible packaging using various additives are also being explored in developed nations to further expand the market.
Sustainability
Concerns for the environment are more potent than ever, with nations at an international level striving to encourage the use and production of products that are sustainable and effective. The rise in popularity of bio-based materials and biodegradable films for the use of flexible packaging increase its appeal. Traditional forms of packaging such as glass, paper, and tin can be replaced with tetra packs, aluminum foils, and PET bottles. Flexible packaging ensures the quality and safety of the products and is also reusable, lessening the demand for increased production of one-time use materials.
Apart from the end-product, the entire life-cycle of flexible packaging has many sustainable advantages. During the manufacturing process of flexible packaging, comparatively lesser natural resources are used, including less water and energy consumption, and fewer emissions of greenhouse gases and volatile organic compounds. Recycled compounds can also be used to manufacture flexible packaging. Since flexible packaging is light-weight, there is less transportation-related consumption of energy and fossil fuels.
The flexible packaging market has steady growth driven by its various applications, regional demands, and sustainability benefits. With the use of additives, the properties of flexible packaging material can be further enhanced. At a time when busy lifestyles are the norm, flexible packaging in the form of sachets, pouches, bags, and liners are of immense convenience and help.